Leverages Operational Accuracy to Strategic Insights
When people think of payroll, they often imagine routine, predictability, and precision. Salaries go out on a specific day, deductions are calculated, taxes are withheld—everything follows a set process. But payroll is far from static. A dynamic flow of numbers is behind the regular cycles, and one of the most critical metrics is variance.
How is variance important in payroll services? It helps payroll professionals spot inconsistencies, control costs, and support real-time decision-making.
Payroll is one of the most sensitive and impactful functions in any organization. It directly affects employee morale, company compliance, and financial health. Payroll is a data-rich domain where variance analysis can unlock major improvements in accuracy, transparency, and strategic planning.
Variance Analysis
Payroll is far from just a back-office function; it is a high-impact, data-rich environment. Small discrepancies can lead to costly mistakes, compliance issues, or even fraud. That’s why understanding payroll variance is not just helpful—it’s essential.
1. Variance as an Accuracy Checkpoint
One of the most common uses of variance analysis in payroll is error detection. Every payroll run involves hundreds or thousands of data points: employee hours, salaries, tax codes, benefits, bonuses, deductions, etc. Even minor errors in these data points can lead to crucial financial mistakes.
Example: An employee’s net pay increases by 15% from the previous month. A variance report highlights it, prompting payroll to discover that a one-time bonus was incorrectly set as recurring.
By monitoring variance at the individual, departmental, and company-wide level, payroll professionals can identify mistakes before they result in costly reprocessing, penalties, or employee dissatisfaction.
2. Aligning Payroll with HR & Finance Strategy
Variance is not just about error-checking—it connects payroll to broader business objectives.
- Workforce Planning: Frequent headcount or cost variances can help HR predict staffing needs more accurately.
- Labor Cost Management: Comparing actual payroll expenses vs. budgeted expenses highlights overstaffing or under-utilization.
- M&A or Restructuring: During organizational changes, variance helps track whether cost reductions and integrations are happening as planned.
Payroll is not isolated—it should be integrated into financial planning and workforce analytics. Variance is the bridge.
3. Ensuring Compliance and Audit Readiness
Payroll is heavily regulated, with strict rules around tax withholding, benefits, and compensation. Unexpected variances can fix issues with:
- Tax calculations
- Benefits administration
- Leave accrual errors
- Misclassification of employees
Keeping a close eye on variance ensures that the payroll function is audit-ready and compliant with labour laws and financial regulations.
4. Supporting Financial Forecasting and Budgeting
Variance does not simply reflect what went wrong—it also helps organizations plan better. Understanding payroll history variance allows HR and finance teams to forecast labour costs more accurately.
- Are overtime costs spiking during certain times of year?
- Is there high variance due to seasonal workers?
- Are headcount fluctuations aligned with business cycles?
These insights help in creating realistic budgets and optimizing workforce planning.
5. Improving Payroll Process Efficiency
A consistent pattern of payroll variances can point to process inefficiencies, such as a delay in updating salary changes in the HR system and decentralized data entry across departments.
By using variance data, payroll teams can refine processes, automate where possible, and reduce manual errors, ultimately improving service delivery.
6. Fraud Detection
Payroll fraud is more common than many assume. Variance reports can highlight unexpected payments, duplicate entries, or employees no longer working with the company.
- Example: If variance shows consistent, unexplained salary increases across a department, it may uncover manipulation by someone within payroll or HR.
Timely detection through variance analysis can save organizations from financial and reputational damage.
What Is Variance in Payroll?
Variance refers to the difference between what was expected or forecasted and what occurred. In payroll, this could relate to:
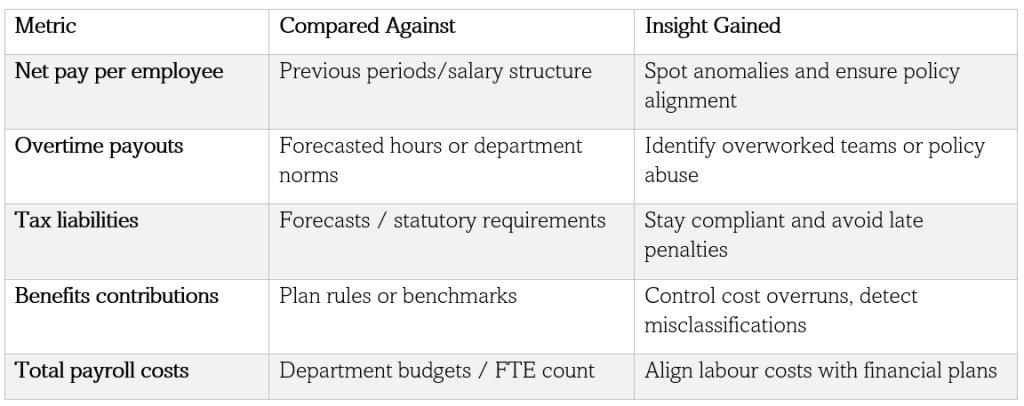
Monthly Payroll Variance Reports: What to Track
Final Thought
In payroll, even a 1% error can lead to significant losses or compliance violations. Variance is not just a number—it’s an early warning system, a strategic tool, and a path to continuous improvement. It plays an evident role in payroll services, making the process seamless and hassle-free.
Payroll professionals who master variance analysis elevate their role from processor to strategic partner. It is a valuable tool for accounting/management officials to monitor the overall business performance and assist in insight-driven decision-making.

is a dedicated Functional Business Analyst at Happiest Minds, with hands-on experience in Finance Automation and Payroll Professional Services projects. With a strong background in identifying and implementing RPA solutions, he excels at analyzing business processes and driving operational efficiency. Known for his problem-solving mindset and collaborative approach, he is an asset to any team aiming to optimize workflows and deliver measurable business value.




